
You must give details of any illness, disability or medical condition you have or have had in your application. Pre-existing conditions, illnesses or disabilities you had before obtaining private health insurance are usually excluded. Exclusions are conditions or circumstances where benefits will not be paid. On the other hand, all private health insurance policies contain some exclusions. CareShield Life, when introduced, is also universal (has no exclusions) for cohorts born in 1980 or later. MediShield Life is universal and has no exclusions. Some health insurance policies provide cover for your whole life, while others cover for a fixed period or up to a certain age. Private insurance plans may have an age limit, and may not be available to you once you reach a certain age. Once enrolled, CareShield Life covers you for life as well. However the minimum age of coverage for CareShield Life is age 30, as it is intended to provide basic coverage for severe disability in old age. There is also no maximum age limit to join CareShield Life when it is introduced in 2020. It covers you for life, and there is no age limit for entry into the scheme.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash-coinsurance-vs-copay-why-you-need-know-difference-final-e570a197e19f4ea58eca928ad5a47c1d.jpg)
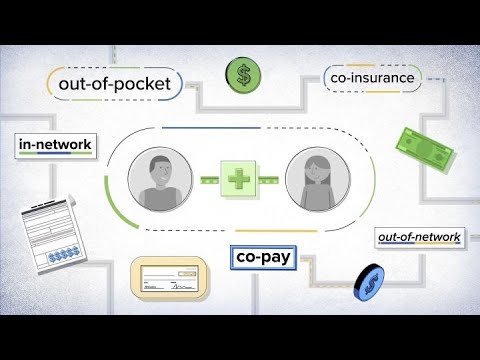
There is no age limit for MediShield Life. At no point will your combined policies pay you more than 100% of your actual medical expenses. For example, limits may be included for all claims as well as for each illness, disability, per month, year, or for a lifetime.įor medical expense insurance, having more policies does not necessarily give you more benefits, as you can claim only up to your actual medical expenses. There are limits to what you can claim under a policy. You can use MediSave up to prevailing limits to pay for the deductible and co-insurance not paid by your insurance policy. For example, if you have a co-insurance of 10%, you will pay 10% of the cost after the deductible. After paying your deductible, you may still have to pay for co-insurance or co-payment.Ĭo-insurance is how much you have to co-pay or split the cost with the insurer after you pay the deductible. Plans with lower premiums usually have higher deductibles. You usually only need to pay the deductible once in a policy year. If you are unable to pay your premiums, your policy may lapse and you will lose coverage.Ī deductible is the initial amount you have to pay for your medical expenses before your health insurance makes a payout. Insurers may choose not to renew a plan or charge a higher premium when there are excessive claims.īefore buying a policy, make sure you can afford the premiums over the long-term. Premiums for health insurance usually increase with age, are not guaranteed and subject to change. It could be a lump sum (single premium) or in smaller sums (regular premiums) every month, quarter or year. The payment to keep your health insurance going is known as a premium.

Start by learning the policy terms that may affect your coverage and claims: So make sure you know exactly what and how much you are covered for. This means you will have to pay for some out-of- pocket medical costs. Most policy features such as deductibles and co-insurance help to keep your premiums affordable.

Health insurance seldom covers 100% of your medical costs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
